Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 23rd June 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- “Decarbonising Transport in India”:
- Initial Public Offer (IPO)
- Senkaku Islands
- China to Join UN Arms Trade Treaty
- Other important current affairs
1.“Decarbonising Transport in India”:

NITI Aayog in collaboration with International Transport Forum (ITF) will launch the “Decarbonising Transport in India” project on 24 June, with the intention to develop a pathway towards a low-carbon transport system for India.
- The “Decarbonising Transport in India” project will design a tailor-made transport emissions assessment framework for India.
- It will provide the government with a detailed understanding of current and future transport activity and the related CO2 emissions as a basis for their decision-making.
Decarbonising Transport in Emerging Economies (DTEE)
- It is part of the “Decarbonising Transport in Emerging Economies” (DTEE) family of projects, which supports transport decarbonization across different world regions. India, Argentina, Azerbaijan, and Morocco are current participants.
- The DTEE is a collaboration between the ITF and the Wuppertal Institute, supported by the International Climate Initiative (IKI) of the German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety.
International Transport Forum (ITF):
- The International Transport Forum at the OECD is an intergovernmental organization with 60 member countries.
- It acts as a think tank for transport policy and organizes the Annual Summit of transport ministers.
- ITF is the only global body that covers all transport modes.
- The ITF is administratively integrated with the OECD, yet politically autonomous.
- India has been a member of ITF since 2008.
2. Initial Public Offer (IPO) :

The Central government has started the process to launch the Initial Public Offer (IPO) of Life Insurance Corporation (LIC).
- LIC is fully owned by the government. It was set up in 1956.
- It has the biggest share in India’s insurance business.
Initial Public Offer
- IPO is the selling of securities to the public in the primary market (a type of capital market).
- The primary market deals with new securities being issued for the first time. It is also known as the new issues market.
- It is different from the secondary market where existing securities are bought and sold. It is also known as the stock market or stock exchange.
- Under IPO, an unlisted company makes either a fresh issue of securities or an offer for sale of its existing securities or both for the first time to the public.
- Through an IPO, an unlisted company can get listed on the stock exchange.
- It is generally used by new and medium-sized firms that are looking for funds to grow and expand their business.
LIC IPO:
- The IPO is expected to be the biggest in the Indian capital markets given the size and scale of LIC.
- The LIC’s total assets had touched an all-time high of Rs. 31.11 lakh crore in 2018-19.
- The government is seeking some exemption related to the LIC IPO from the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- It will help the government to meet its rising fiscal deficit.
- The rating agency S&P has estimated India’s government (center and states) fiscal deficit to rise to 11% of GDP in FY21 from 7.8% in FY20.
- An IPO will bring transparency into affairs of LIC since it will be required to inform its value and other market-related developments on time to the stock exchanges.
- It also gives an opportunity for retail investors to participate in the wealth creation of LIC.
- Listing of companies on stock exchanges disciplines the company since it comes under greater scrutiny. It also provides access to financial markets, thus raising the company’s value.
LIC is currently dealing with huge non-performing assets.
- In the Budget 2020-21, the government had announced plans for IPO of LIC and a proposal to sell the government’s equity in the stressed IDBI Bank to private, retail and institutional investors through the stock exchange.
3.Senkaku Islands:
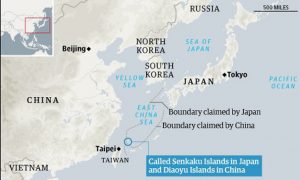
Recently, a local council in southern Japan has approved a bill to change the name of an area containing the Senkaku Islands from Tonoshiro to Tonoshiro Senkaku.
- Senkaku Islands are known as the Diaoyus by China and Tiaoyutai by Taiwan.
- The islands are disputed with China and Taiwan.
- A local council- assembly of Ishigaki city- in southern Japan has voted to rename an area, including islands disputed with China and Taiwan, a move Beijing denounced as illegal and “serious provocation”.
- It has approved a plan to change the name of the area covering the Tokyo-controlled Senkaku Islands — known by Taiwan and China as the Diaoyus — from “Tonoshiro” “Tonoshiro Senkaku”.
- The uninhabited islands are at the center of a festering row between Tokyo and Beijing.
- Besides, Taiwan says the islands are part of its territory, and also protested the move.
Senkaku Islands:
- The Senkaku Islands are located in the East China Sea between Japan, the People’s Republic of China, and the Republic of China (Taiwan). The archipelago contains five uninhabited islands and three barren rocks, ranging in size from 800 m2 to 4.32 km2.
- The Senkaku Islands were not included in the territory which Japan renounced under Article 2 of the San Francisco Peace Treaty of 1951 that legally defined the territory of Japan after World War II.
- Under Article 3 of the treaty, the islands were placed under the administration of the United States as part of the Nansei Shoto Islands.
- The Senkaku Islands are included in the areas whose administrative rights were reverted to Japan in accordance with the Agreement between Japan and the United States of America Concerning the Ryukyu Islands and the Daito Islands that entered into force in 1972.
China says that the islands have been part of its territory since ancient times, serving as important fishing grounds administered by the province of Taiwan.
Taiwan was ceded to Japan in the Treaty of Shimonoseki in 1895, after the Sino-Japanese war.
4.China to Join UN Arms Trade Treaty:

Recently, China has decided to join the United Nations Arms Trade Treaty (UN-ATT) to regulate its arms sales.
- China held that it has always strictly controlled the export of military products and joining the treaty is an important step towards its efforts to enhance peace and stability in the world and support multilateralism.
- China said that it only exports military products to sovereign countries and not to non-state actors.
- China’s move comes after the USA announced to pull out of the ATT in 2019.
- The reason given was that the treaty amounts to international gun control, and is a threat to the USA’s second amendment right to bear arms.
- The USA also held that the treaty fails to truly address the problem of irresponsible arms transfers because other top arms exporters like Russia and China were not signatories to it that time (till now, Russia has neither signed it nor made any announcement to sign it).
- In May 2020, the USA announced to exit the Open Skies Treaty (OST).
- In August 2019, the USA along with Russia withdrew from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty, 1987.
- The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) in its annual report ‘Trends in World Military Expenditure, 2019’ highlighted that China is the second-largest arms producer in the world after the USA.
United Nations Arms Trade Treaty
- The UN-ATT regulates the international trade in conventional arms, from small arms to battle tanks, combat aircraft, and warships, and controls the flow of weapons into conflict zones.
- It entered into force on 24th December 2014.
- The treaty requires member countries to keep records of international transfers of weapons and to prohibit cross-border shipments that could be used in human rights violations or attacks on civilians.
- State parties to the treaty may seek assistance in its implementation and the UN Trust Facility Supporting Cooperation on Arms Regulation (UNSCAR) was launched to help in that.
Other important current affairs:
1. The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) has busted a wildlife smuggling syndicate with the seizure of a consignment of exotic macaws which had been smuggled from Bangladesh to Kolkata. The exotic birds were identified as Hyacinth macaw, Pesquet’s parrot, Severe macaw, and Hahn’s macaw.
- Common Name: Macaws.
- Scientific Name: Psittacidae.
- Family: Macaws are beautiful, brilliantly colored members of the parrot family.
- Distribution: Macaws are native to Central America and North America (only Mexico), South America, and formerly the Caribbean. Most species are associated with forests, especially rainforests, but others prefer woodland or savannah-like habitats.
- There are at least 17 species of macaws, and several are endangered. The glaucous macaw and Spix’s macaw may already be extinct in the wild.
- The macaws are protected under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), with Hyacinth macaw being accorded the highest protection.
2. A medium-intensity earthquake of 5.1 magnitudes rocked Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur and the other northeastern States on 21st June.
- As per the seismic hazard map of India, both the states of Mizoram and Tripura lie entirely in Zone V.
- Also, in Mizoram, lie the southernmost end of the Purvanchal Himalayan range. Their folded structure is a synclinorium consisting of broad synclines and tight-faulted anticlines.
- Therefore, earthquakes in this region are generally shallow, though a few quakes of intermediate-depth have occurred.
- Most deeper earthquakes occur along and across the international border, in Myanmar’s Chin Division. Earthquake activity in Tripura is mainly shallow.
- The Dauki Fault which follows the international border of India and Bangladesh in Meghalaya passes through northern sections of Tripura.
- The other major threat is from the Madhupur Fault in Bangladesh.
3. International Widows Day is being observed on 23 June.
- The United Nations observes 23 June as International Widows Day (resolution A/RES/65/189) since 2011, to draw attention to the voices and experiences of widows and to galvanize the unique support that they need.
- There are an estimated 258 million widows around the world, and nearly one in ten live in extreme poverty.
- The Ministry of Rural Development is implementing Indira Gandhi National Widow Pension Scheme (IGNWPS) under which the Pension Scheme for Widows as well as Pension Scheme for the Elderly below the poverty line is operated.
- A Home for Widows has been set up in Vrindavan, UP with a capacity of 1000 inmates to provide widows a safe and secure place of stay, health services, nutritious food, legal, and counseling services.
- The Ministry of Defence provides financial assistance for vocational training of widows of ex-servicemen, treatment of serious diseases of non-pensioner ex-servicemen/widows and daughter’s marriage/widows’ remarriage.
4.UN Public Service Day 2020 is being observed on June 23 to honor public servants in the COVID-19 pandemic response.
- On 20 December 2002, the General Assembly designated 23 June as Public Service Day by adopting resolution 57/277.
- UN Public Service Day highlights the contribution of public service in the development process and recognizes the work of public servants.
- The prestigious UN Public Service Awards (UNPSA) are given away on this day by the United Nations Economic and Social Council for contributions made to the cause of enhancing the role, prestige, and visibility of public service.
- The day also marks the anniversary of the date when the International Labour Organization adopted the Convention on Labour Relations (Public Service), 1978 (No. 151). This Convention is a framework for determining the working conditions of all civil servants across the world.
5. The Finance Ministry has given approval to a proposal to allow individuals and institutions to contribute directly to the National Disaster Relief Fund (NDRF).
- This is a significant development at a time when many have expressed concerns about donations sent to the PM CARES Fund or the Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund, as both claim they are not public authorities subject to questions under the Right to Information Act.
- The NDRF was set up in accordance with Section 46 of the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- It is meant to “meet the expenses for emergency response, relief and rehabilitation” for any disaster situation.
- Although Section 46 includes a clause for grants made by any person or institution, provisions for such donations had not been made.
6. Skeletal remains of a child were excavated from Konthagai village, part of the sixth phase of ongoing excavations in the ancient site of Keeladi. Konthagai village, located around 2 km from Keeladi, is believed to be a burial site.
- Keeladi excavation site is a Sangam period settlement that is being excavated by the Archaeological Survey of India and the Tamil Nadu Archaeology Department.
- The settlement lies on the bank of the Vaigai River. This site is located 12 km southeast of Madurai in Tamil Nadu, near the town of Keeladi in Sivagangai district. This is a large-scale excavation carried out in Tamil Nadu after the Adichanallur archaeological site.
- This site is estimated to be from the period between the 5th century BCE and 3rd century CE.
7. Jharkhand is set to launch a 100-day employment scheme for urban unskilled workers similar to the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) amid the coronavirus pandemic and increasing unemployment.
- Recently the Government of India has launched a rural public works scheme ‘Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan’ to provide livelihood opportunities to the returnee migrant workers and rural citizens.
- Even Jharkhand launched three employment schemes earlier to create wage employment for workers in rural areas. In this context, an employment guarantee scheme for the urban poor is a unique and timely intervention.
- The scheme will be known as Mukhyamantri SHRAMIK (Shahri Rozgar Manjuri For Kamgar) Yojana.
- Objective: Enhancing livelihood security for the urban poor.
- They will be given priority in the existing schemes. If they could not be accommodated in existing schemes, exclusive schemes for the purpose will be created and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) would be given separate funds for this.
- Basic Provisions:
- The workers will be able to demand work either in writing or orally for a minimum of seven days and a maximum of 100 days.
- If a worker has a child of five years or less, then a female worker will need to be employed—to take care of the child—and paid the minimum wage. All basic amenities, medical facilities, registration as well as social security will be provided.




