Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:19th March 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Indira Gandhi Matritva Poshan Yojana
- COVID-19 pandemic :
- Open Market Operations:
- National Commission for Indian Systems of Medicine (NCIM) Bill, 2019
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana
- UN Security Council
- Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of Beggars
- Herd community
- Call data records (CDRs):
- Contact tracing
- Other important current affairs
1.Indira Gandhi Matritva Poshan Yojana:

The scheme was recently announced by the Rajasthan Government on a pilot basis in 4 districts.
- The scheme will be implemented in Udaipur, Pratapgath, Banswara, and Dungarpur, where nutrition indicators among children and anemia levels among mothers are worse than the average for the State.
- It is a maternity benefit scheme.
- Under the scheme ₹, 6,000 will be offered for the birth of the second child.
- The government aims to reach out to 75,000 beneficiaries annually. It estimates an expenditure of ₹45 crores per year.
- The State scheme will complement the Central government’s Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana which offers ₹5,000 for the birth of the first child.
- The government feels that the second child doesn’t receive as much attention as the first child and, therefore, it is important to extend this cash benefit to ensure adequate nutrition for the second child.
2.COVID-19 pandemic :

The International Labour Organization (ILO) has recently said that the COVID-19 pandemic will drastically increase global unemployment, leaving up to 25 million more people out of work and slashing incomes.
- COVID-19 is not only a global health crisis but also a major labour market and economic crisis that is having a huge impact on people.
- The International Labour Organization (ILO), has warned that the economic and labour crisis sparked by the coronavirus will have far-reaching impacts on labour market outcomes.
- The ILO said that by comparison, the global financial crisis of 2008-09 increased global unemployment by 22 million.
- A study based on the report suggests that the world should prepare to see a significant rise in unemployment and underemployment in the wake of the pandemic.
- In the best-case scenario, 5.3 million more people will be pushed into unemployment.
- In the worst-case scenario, 24.7 million more will become jobless, on top of the 188 million registered as unemployed in 2019.
- Underemployment is also expected to increase on a large scale, as the economic consequences of the virus outbreak translate into reductions in working hours and wages.
- Self-employment in developing countries usually serves to cushion the impact of economic shifts but this time due to the severe restrictions on the movement of people and goods, it might not help
- Reductions in access to work will also mean large income losses for workers.
- The study estimates the income loss between $860 billion and $3.4 trillion by the end of 2020, which will translate into falls in consumption of goods and services, in turn affecting the prospects for businesses and economies.
- The number of people who live in poverty despite holding one or more jobs will also increase significantly.
- The strain on incomes resulting from the decline in economic activity will devastate workers close to or below the poverty line.
- Some groups will be disproportionately impacted by the jobs crisis, including youth, older workers, women and migrants which will only increase the already prevailing inequality.
3.Open Market Operations:

Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has decided to infuse Rs.10,000 crore liquidity in the banking system by buying government securities through Open Market Operations (OMO).
- The financial markets have been facing heightened volatility due to the spread of the COVID-19.
- RBI had earlier infused Rs. 25,000 crore of liquidity through Long-Term Repo Operations (LTRO).
- Open Market Operations (OMOs) are market operations conducted by RBI by way of sale/purchase of government securities to/from the market with an objective to adjust the rupee liquidity conditions in the market on a durable basis.
- If there is excess liquidity, RBI resorts to sale of securities and sucks out the rupee liquidity.
- Similarly, when the liquidity conditions are tight, RBI buys securities from the market, thereby releasing liquidity into the market.
- It is one of the quantitative (to regulate or control the total volume of money) monetary policy tools which is employed by the central bank of a country to control the money supply in the economy.
- Under LTRO, RBI will conduct term repos of one-year and three-year tenors of appropriate sizes for up to a total amount of Rs 1 lakh crore at the prevailing repo rate.
- As banks get long-term funds at lower rates, their cost of funds falls. In turn, they reduce interest rates for borrowers.
- LTRO helps RBI to ensure that banks reduce their marginal cost of funds-based lending rate, without reducing policy rates.
4.National Commission for Indian Systems of Medicine (NCIM) Bill, 2019:

Recently, the Rajya Sabha passed the National Commission for Indian Systems of Medicine (NCIM) Bill, 2019 and the National Commission for Homeopathy Bill, 2019 for setting up separate commissions for Indian traditional systems of medicine and homeopathy respectively.
- The National Commission for Indian Systems of Medicine (NCIM) Bill, 2019 seeks to replace the existing regulator Central Council for Indian Medicine (CCIM) with a new body to ensure transparency.
- Whereas, the National Commission for Homeopathy Bill, 2019, aims to replace the Central Council for Homeopathy, which is the current regulatory body for homeopathy.
- The two legislations aim to ensure the availability of quality medical professionals of Indian systems of medicine and homeopathy.
- The Bills also intend to adopt and integrate the latest research with traditional medicines.
Loopholes: - Exclusion of yoga and naturopathy from the ambit of the National Commission for Indian System of Medicine.
- Absence of an appellate tribunal for both the commissions.
- Lack of integration of modern and traditional medical education.
5.Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana:

Recently, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has informed about the implementation of the Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY) in the country.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana is the scheme of the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
- It was launched in 2017.
- It is a central sector scheme funded by the Senior Citizens’ Welfare Fund. The fund was notified in the year 2016.
- All unclaimed amounts from small savings accounts, PPF and EPF are transferred to this fund.
- It aims to provide aids and assistive living devices to senior citizens belonging to the Below Poverty Line (BPL) category who suffer from age-related disabilities such as low vision, hearing impairment, loss of teeth and locomotor disabilities.
- The aids and assistive devices, viz walking sticks, elbow crutches, walkers/crutches, tripods/quad pods, hearing aids, wheelchairs, artificial dentures, and spectacles are provided to eligible beneficiaries.
- The scheme is being implemented by Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO), which is a public sector undertaking under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
6.UN Security Council:

Recently, China has taken over as president of the UN Security Council for the month of March 2020.
- The Security Council was established by the UN Charter in 1945.
- It is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
- The other 5 organs of the United Nations are—the General Assembly, the Trusteeship Council, the Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Secretariat.
- Its primary responsibility is to work to maintain international peace and security.
- The council has 15 members: the five permanent members and 10 non-permanent members elected for two-year terms.
- The five permanent members are the United States, the Russian Federation, France, China and the United Kingdom.
- Each member of the Security Council has one vote.
- Decisions of the Security Council on matters are made by an affirmative vote of nine members including the concurring votes of the permanent members. A “No” vote from one of the five permanent members blocks the passage of the resolution.
- Any member of the United Nations which is not a member of the Security Council may participate, without a vote, in the discussion of any question brought before the Security Council whenever the latter considers that the interests of that Member are especially affected.
- The council’s presidency is a capacity that rotates every month among its 15 members.
- The council is headquartered in NewYork.
7. Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of Beggars”.:

The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has proposed to restructure & formulate a scheme namely “Scheme for Comprehensive Rehabilitation of Beggars”.
- It will be a comprehensive scheme for persons engaged in the Act of begging which would cover identification, rehabilitation, provision of medical facilities, counseling, education, skill development with the support of State Governments/UTs/Local Urban Bodies and Voluntary Organizations.
- The scheme will be implemented in the selected cities having a large concentration of the Beggar community during the financial year 2020-2021.
- 100% Assistance under the Scheme shall be provided to the States/UTs for its implementation.
8.Herd Immunity’:
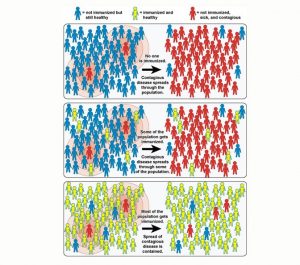
UK has retracted under criticism after suggesting it would allow COVID-19 to pass through the population, so that ‘herd immunity’ could be achieved.
- Herd immunity refers to preventing an infectious disease from spreading by immunizing a certain percentage of the population.
- While the concept is most commonly used in the context of vaccination, herd immunity can also be achieved after enough people have become immune after being infected.
- The premise is that if a certain percentage of the population is immune, members of that group can no longer infect another person.
- This breaks the chain of infection through the community (“herd”) and prevents it from reaching those who are the most vulnerable.
- “Herd immunity threshold” is the number of immune individuals above which a disease may no longer circulate.
- However, the discussion on herd immunity to fight COVID-19 in the UK has not been based on this conventional definition.
- The UK government had wanted the entire population to be exposed to the novel coronavirus infection so that the majority could develop immunity to COVID-19.
9. Call data records (CDRs):
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has been asking operators to call data records (CDRs) by the bulk. The government seeking such details on specific dates for certain pockets in the country without mentioning the reason is highly unusual.
- A Call Data Record (CDR) of a subscriber is a string of information about that mobile phone number for a particular time period.
- This string of information includes details such as the name of the subscriber, the details of calls made by this subscriber during a given time period, the duration of each call, whether the call terminated normally or abnormally, rough location of the caller, etc.
- Under the new guidelines, only an officer of the rank of SP and above was authorized to seek details from telecom operators, and inform the DM of CDRs obtained every month.
- The current request is not in line with these guidelines.
11.Contact tracing:
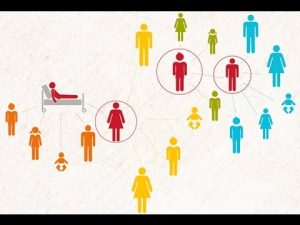
Beginning from the second phase of the epidemic when local transmission takes place contact tracing is an integral part of fighting the epidemic on the ground
- People in close contact with someone who is infected with a virus are at higher risk of becoming infected themselves, and of potentially further infecting others.
- Contract tracing is the process of identifying, assessing, and managing people who have been exposed to a disease to prevent transmission.
This process can be broken down into 3 basic steps:
- Contact identification: Once someone is confirmed as infected with a virus, contacts are identified by asking about the person’s activities and the activities and roles of the people around them since the onset of illness.
- Contact listing: All persons considered to have contact with the infected person should be listed as contacts and informed them of their contact status.
- Contacts should also be provided with information about the prevention of the disease.
- Contact follow-up: Regular follow-up should be conducted with all contacts to monitor for symptoms and test for signs of infection.
Other important current affairs:
1. Recently, the Supreme Court invoked its special powers under Article 142 of the Constitution to remove a Manipur minister.
- The Supreme Court removed Thounaojam Shyamkumar Singh, from the state cabinet and restrained him “from entering the Legislative Assembly till further orders”.
- A disqualification petition against the minister was pending before the Speaker since 2017 but the Speaker failed to take the decision within a reasonable time period.
- The Speaker also failed to take any decision within the stipulated time period of 4 weeks as provided by the Supreme Court in the 21st January 2020 order.
- Article 212 of the Constitution bars courts from inquiring into proceedings of the Legislature. In this case, however, prompted by the fact that the Speaker’s conduct has been called into question on several occasions, the Court said it was “constrained” to invoke the court’s extraordinary powers under Article 142 of the Constitution.
3. The Real-time Train Information system is being installed in locomotives to enable better tracking of train movement.
- The RTIS Project is being executed by the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS) in collaboration with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- RTIS is an example of ‘Make In India’ as it has been entirely designed, developed and manufactured within the country.
- RTIS enables automatic acquisition of train movement timings at the stations, including that of arrival & departure or run-through.
- It also helps in the automatic plotting of control charts in ICT based Control Office Application (COA) on all divisions of Indian Railways.
3. A petition was recently filed in the Supreme Court conveying “widespread disquiet and unease” triggered by the nomination of the former Chief Justice of India Ranjan Gogoi to the Rajya Sabha.
- The petition sought the court’s intervention for extending the post-retirement restrictions imposed on the office of the Lokpal to former judges as well.
- The petition said former judges should be insulated from “post-retirement allurements” like the Lokpal, as faith in the judiciary will dry up.
- There is no law or constitutional provision that prohibits such a nomination. Nor is this an unprecedented decision by the government.
- Still, it is not a common practice that a government nominates or appoints a former Supreme Court judge or even a high court judge to some office within months of her or his retirement.
- Currently, the only bar imposed on a Judge of the Supreme Court who has retired is that he shall not thereafter plead or act in any Court or before any authority.
5. Union Home Ministry has filed an affidavit in the Supreme Court stating that the preparation of NRC is a “necessary exercise for any sovereign country for mere identification of citizens from non-citizens.”
- It is the responsibility entrusted with the Central government “to identify/detect illegal migrants and thereafter, follow the due process of law”.
- The Foreigners Act, 1946, confers upon the government the power to expel foreigners from India.
- It vests the Central government with absolute and unfettered discretion, and as there is no provision fettering this discretion in the Constitution, an unrestricted right to expel remains.
- More than a dozen States have vociferously opposed the updating of National Population Register (NPR), slated to begin on April 1 along with the house listing phase of the Census. According to Citizenship Rules 2003, NPR is the first step towards the compilation of the NRC.
- There are fears that the CAA, followed by a country-wide NRC, will benefit non-Muslims excluded from the citizens’ register, while excluded Muslims will have to prove their citizenship.
- The government has denied that CAA and NRC are linked.
6. Defense Acquisition Council (DAC):
- To counter corruption and speed up decision- making in military procurement, the government of India in 2001 decided to set up an integrated DAC.
- It is headed by the Defence Minister.
- The objective of the DAC is to ensure expeditious procurement of the approved requirements of the Armed Forces, in terms of capabilities sought, and the time frame prescribed, by optimally utilizing the allocated budgetary resources.
- The DAC is responsible to give policy guidelines to acquisitions, based on long-term procurement plans. It also clears all acquisitions, which includes both imported and those produced indigenously or under a foreign license.
7. The World Health Organisation (WHO) advised patients suffering from COVID-19-like symptoms to avoid the anti-inflammatory drug ibuprofen unless prescribed by doctors, as it may make patients more vulnerable to COVID-19.
- Ibuprofen is an anti-inflammatory drug. Common medicines that contain ibuprofen include Brufen and Combiflam tablets.
- Ibuprofen, a non-steroid, is used for relief from joint pain, migraine, fever, body ache, and even pain during the menstrual cycle. Its function is to reduce pain, swelling, and fever by suppressing substances that produce swelling in the body.
- Other non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) include aspirin, cortisone, naproxen, and diclofenac.
8. The Lok Sabha is discussing supplementary demands for grants for 2019-20. This includes 78 grants and four appropriations.
- If the government needs to spend any additional money, it can introduce Supplementary Demands for Grants during the year. The additional grant required to meet the required expenditure of the government is called Supplementary Grants.
- When grants, authorized by the Parliament, fall short of the required expenditure, an estimate is presented before the Parliament for Supplementary or Additional grants. These grants are presented and passed by the Parliament before the end of the financial year.
- When actual expenditure incurred exceeds the approved grants of the Parliament, the Ministry of Finance presents a Demand for Excess Grant. The Comptroller and Auditor General of India bring such excesses to the notice of the Parliament.
- The Public Accounts Committee examines these excesses and gives recommendations to the Parliament. The Demand for Excess Grants is made after the actual expenditure is incurred and is presented to the Parliament after the end of the financial year in which the expenses were made.
9.IHBT scientists develop new sanitizer without chemicals like parabens, triclosan, and phthalates.
- A new hand-sanitizer has been developed by the scientists of CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology (CSIR-IHBT) based in Palampur, Himachal Pradesh.
- The natural flavors, active tea constituents and alcohol content in this hand-sanitizer have been used as per the guidelines of the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Chemicals like parabens, triclosan, synthetic fragrance, and phthalates have not been used in this product.
- The technology has been transferred to Palampur based company M/s A.B. Scientific Solutions for the commercial production of this newly developed hand-sanitizer.
- An agreement has been signed between CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology (CSIR-IHBT) and the company.
10. In a big boost to ‘Make in India’, Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) cleared the acquisition of 83 indigenous Tejas fighter aircraft for Indian Air Force (IAF) with more advanced configuration than the 40 currently on order.
- The Light Combat Aircraft Tejas has been indigenously-designed by Aircraft Development Agency (ADA) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- While orders of 40 Tejas aircraft had been placed with HAL in initial configurations, DAC paved the way for procurement of 83 of the more advanced Mk1A version of the aircraft from HAL by finalizing the contractual and other issues.
- The proposal will now be placed for consideration of the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS).
10. The Minister of Textiles Smt Smriti Irani presented the details of the National Technical Textiles Mission at Rajya Sabha. The GoI has allocated Rs 1,480 crores for the mission
- The Mission aims to improve technical textiles in India.
- The mission is to be implemented for a period of 4 years between 2020-21 and 2023-24.
- It is to be implemented by the Ministry of Textiles.




